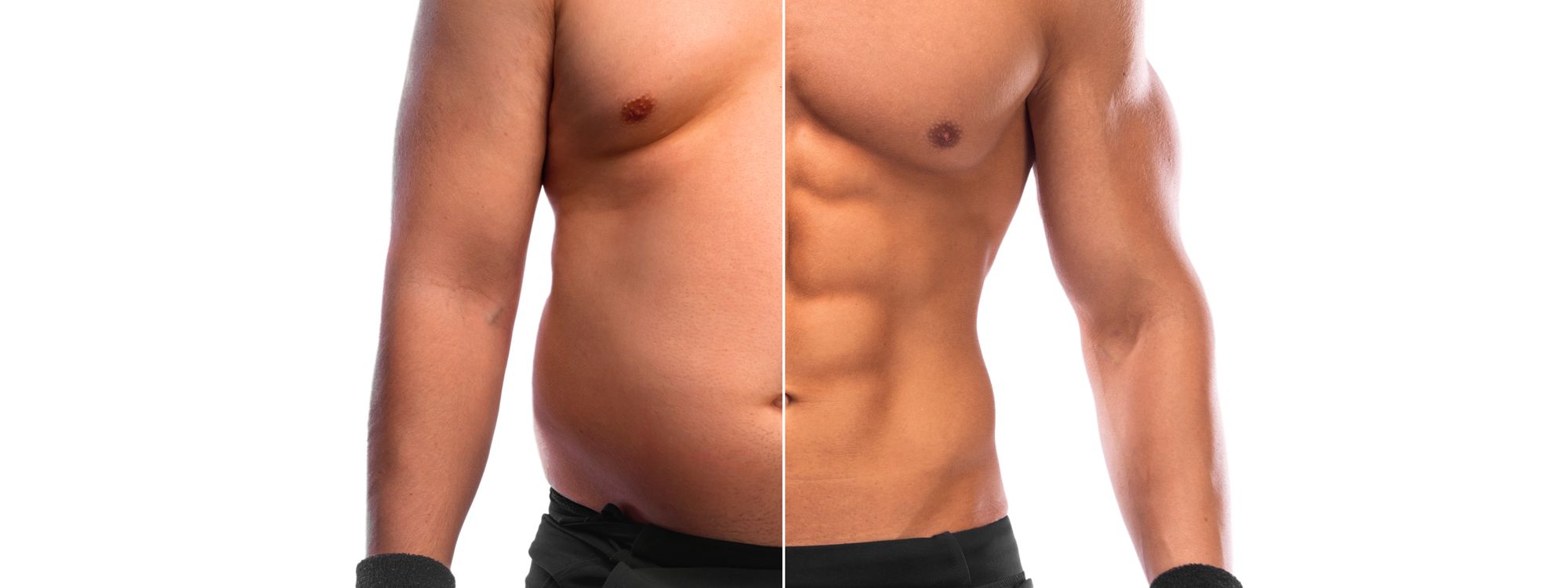
Body recomposition diet focuses on losing fat while gaining muscle through strategic macronutrient ratios, nutrient timing, and strength training, emphasizing patience and consistency for optimal results.
Body recomp
Body recomp, short for body recomposition, refers to the process of simultaneously losing fat and gaining muscle. It typically involves adjusting nutrition, focusing on macronutrient ratios—especially protein—while incorporating strength training. The goal is to improve body composition, emphasizing aesthetics and overall fitness rather than just weight loss. Success in body recomp requires a careful balance of caloric intake and expenditure, alongside progressive resistance training and adequate recovery. Monitoring progress through measurements and performance rather than solely the scale is crucial for achieving desired results approach to weight loss
Body Recomposition Workout Plan
Here’s a sample body recomposition workout plan designed to help you build muscle while losing fat. This plan combines strength training, cardio, and flexibility work over the course of a week.
Weekly Workout Plan
Day 1: Upper Body Strength
- Warm-up: 5-10 minutes of dynamic stretches or light cardio
- Bench Press: 4 sets of 6-8 reps
- Pull-Ups/Lat Pulldowns: 4 sets of 6-8 reps
- Dumbbell Shoulder Press: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Bent-over Rows: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Bicep Curls: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Tricep Dips: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Cool Down: Stretching
Day 2: Lower Body Strength
- Warm-up: 5-10 minutes of dynamic stretches
- Squats (Back or Front): 4 sets of 6-8 reps
- Deadlifts (Conventional or Romanian): 4 sets of 6-8 reps
- Lunges (Walking or Stationary): 3 sets of 10 reps per leg
- Leg Press or Leg Curl: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Calf Raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Cool Down: Stretching
Day 3: Cardio and Core
- Cardio: 20-30 minutes of HIIT (e.g., sprints, cycling, rowing)
- Core Workout:
- Planks: 3 sets of 30-60 seconds
- Russian Twists: 3 sets of 15 reps per side
- Leg Raises: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Cool Down: Stretching
Day 4: Full Body Strength
- Warm-up: 5-10 minutes of dynamic stretches
- Clean and Press: 4 sets of 6-8 reps
- Kettlebell Swings: 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Push-Ups: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Dumbbell Snatch: 3 sets of 8-10 reps per arm
- Plank to Push-Up: 3 sets of 6-8 reps
- Cool Down: Stretching
Day 5: Active Recovery
- Light Cardio: 20-30 minutes (walking, cycling)
- Flexibility Work: Yoga or stretching routine
Day 6: Repeat Day 1 or Day 2 (Upper/Lower Split)
- Depending on your schedule, you can repeat either the upper or lower body workout from earlier in the week.
Day 7: Rest Day
- Focus on recovery, hydration, and nutrition.
Tips for Success
- Nutrition: Ensure adequate protein intake (aim for 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kg of body weight) and maintain a balanced diet.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated before, during, and after workouts.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support recovery.
- Listen to Your Body: Adjust weights and intensity based on your fitness level and progress.
Body Recomposition
Body recomposition is the process of simultaneously losing fat and gaining muscle, ultimately improving body composition rather than just focusing on weight loss. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Key Principles of Body Recomposition
- Nutrition:
- Protein Intake: Aim for high protein consumption (1.6 to 2.2 grams per kg of body weight) to support muscle growth and repair.
- Caloric Balance: Create a slight caloric deficit for fat loss while having strategic surpluses around workouts to promote muscle growth.
- Strength Training:
- Progressive Overload: Continuously increase weights or resistance to challenge muscles.
- Compound Exercises: Focus on multi-joint movements like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups to maximize muscle engagement.
- Cardiovascular Exercise:
- Incorporate HIIT: High-Intensity Interval Training can be effective for fat loss while preserving muscle.
- Steady-State Cardio: Moderate-intensity cardio can help with overall calorie expenditure and cardiovascular health.
- Recovery:
- Rest Days: Allow muscles time to recover and grow.
- Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep (7-9 hours) for optimal recovery and hormone regulation.
- Monitoring Progress:
- Use body measurements, progress photos, and strength gains as indicators of progress rather than just relying on the scale.
Benefits of Body Recomposition
- Improved muscle definition and tone
- Enhanced metabolic rate
- Increased strength and athletic performance
- Better overall health and body image
Recomp
Recomp,” short for body recomposition, refers to the process of simultaneously losing fat and gaining muscle
Body recomposition, often referred to as “recomp,” is an increasingly popular fitness strategy that aims to help individuals lose fat while simultaneously gaining muscle. Unlike traditional weight loss approaches that focus solely on losing pounds, recomp emphasizes changing your body composition for improved aesthetics and health. In this blog, we’ll explore the key components, benefits, and practical tips for achieving successful body recomposition.
Body Recomposition Diet
A body recomposition diet focuses on simultaneously losing fat and gaining muscle. Here’s a breakdown of how to effectively structure your diet for optimal results.
Key Principles of a Body Recomposition Diet
- Prioritize Protein:
- Why: Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth.
- How Much: Aim for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Include sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins.
- Manage Macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: Carbs provide energy for workouts and recovery. Focus on complex carbohydrates (whole grains, fruits, vegetables) and adjust intake based on activity level.
- Fats: Include healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil) for overall health and hormone regulation. Aim for fats to comprise about 20-30% of your total caloric intake.
- Caloric Balance:
- Slight Deficit: Create a small caloric deficit (around 250-500 calories) for fat loss while ensuring you consume enough around workouts to support muscle gain.
- Caloric Cycling: Consider varying your caloric intake throughout the week. Higher intake on training days and lower on rest days can optimize both fat loss and muscle gain.
- Nutrient Timing:
- Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition: Consume a balanced meal or snack with protein and carbs before and after workouts to fuel performance and aid recovery.
- Regular Meals: Aim for 4-6 balanced meals/snacks throughout the day to keep energy levels stable and support muscle growth.
- Hydration:
- Stay well-hydrated, as water is crucial for metabolic processes, performance, and recovery. Aim for at least 2-3 liters per day, adjusting for activity levels.
Sample Meal Plan for Body Recomposition
Breakfast:
- Scrambled eggs (3 whole eggs) with spinach and tomatoes
- Oatmeal topped with berries and a tablespoon of almond butter
Snack:
- Greek yogurt with a scoop of protein powder and a banana
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and a side of mixed vegetables (broccoli, carrots, bell peppers)
- Olive oil and lemon dressing
Snack:
- Hummus with carrot and cucumber sticks
Dinner:
- Baked salmon with sweet potatoes and steamed asparagus
- Mixed green salad with olive oil and vinegar
Evening Snack (if needed):
- Cottage cheese with a sprinkle of cinnamon and a handful of nuts
Tips for Success
- Track Your Intake: Use apps or journals to monitor your macronutrient and caloric intake.
- Meal Prep: Preparing meals in advance can help you stick to your diet and avoid unhealthy choices.
- Be Patient: Body recomposition is a gradual process. Focus on consistency rather than immediate results.
- Adjust as Needed: Monitor your progress and be willing to tweak your diet based on results.
What Is Body Recomposition
Body recomposition refers to the process of simultaneously losing fat and gaining muscle. Unlike traditional approaches to fitness that focus on either weight loss or muscle gain individually, body recomposition targets both goals at once. The main idea is to change your body composition — the ratio of fat to lean mass — without necessarily focusing on the number on the scale.
Here’s how body recomposition generally works:
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or engaging in resistance training to build and maintain muscle.
- Protein Intake: Consuming adequate protein to support muscle growth and recovery, especially in a calorie deficit.
- Calorie Control: Eating at or slightly below maintenance calories to encourage fat loss while still providing enough nutrients for muscle growth.
- Consistency: It’s a slower process than either bulking or cutting alone, so consistency over time is crucial.
Body recomposition diet is popular among those who want to look leaner and more muscular without major fluctuations in weight.